Bootstrap Grid HTML
Introduction
Bootstrap provides a powerful mobile-first flexbox grid solution for building designs of any scales and shapes . It is simply built upon a 12 column layout and comes with plenty of tiers, one for every media query selection. You can certainly utilize it with Sass mixins or of the predefined classes.
One of the most important part of the Bootstrap framework helping us to develop responsive website page interactively transforming to regularly fit the size of the screen they get revealed on still looking nicely is the so called grid system. Things that it generally executes is providing us the capability of generating complicated arrangements integrating row plus a specific quantity of column elements stored inside it. Think of that the detectable size of the display screen is split up in twelve same components vertically.
The best ways to put into action the Bootstrap grid:
Bootstrap Grid Template employs a series of columns, containers, and rows to format and fix material. It's developed through flexbox and is entirely responsive. Listed here is an example and an in-depth explore just how the grid interacts.
The above illustration generates three equal-width columns on little, medium, big, and extra sizable devices applying our predefined grid classes. All those columns are focused in the web page with the parent
.containerHere is actually in what way it does work:
- Containers deliver a way to center your web site's items. Apply
.container.container-fluid- Rows are horizontal sets of columns which make sure your columns are really aligned correctly. We work with the negative margin method on
.row- Web content should really be positioned within columns, and also just columns may possibly be immediate children of rows.
- Thanks to flexbox, grid columns without having a established width will instantly layout with equal widths. As an example, four instances of
.col-sm- Column classes signify the amount of columns you 'd like to use outside of the potential 12 per row. { In such manner, on the occasion that you really want three equal-width columns, you can employ
.col-sm-4- Column
widths- Columns feature horizontal
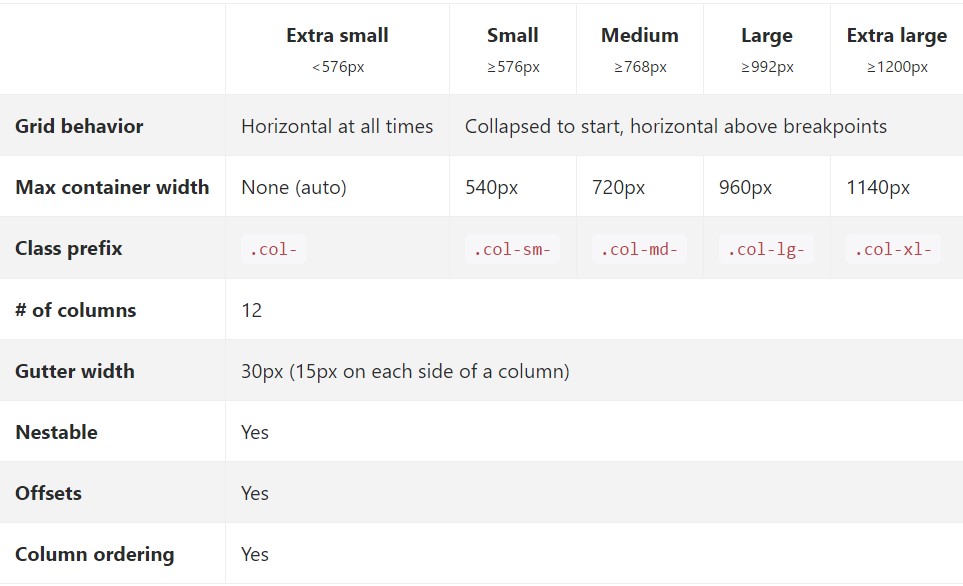
paddingmarginpadding.no-gutters.row- There are 5 grid tiers, one for every responsive breakpoint: all breakpoints (extra small-sized), small, medium, large size, and extra large.
- Grid tiers are formed on minimal widths, meaning they concern that one tier and all those above it (e.g.,
.col-sm-4- You have the ability to work with predefined grid classes as well as Sass mixins for more semantic markup.
Recognize the issues and bugs around flexbox, like the inability to utilize several HTML elements as flex containers.
Sounds awesome? Outstanding, let us go on to noticing everything in an instance. ( additional reading)
Bootstrap Grid CSS solutions
Generally the column classes are something like that
.col- ~ grid size-- two letters ~ - ~ width of the element in columns-- number from 1 to 12 ~.col-When it approaches the Bootstrap Grid Table scales-- all of the workable sizes of the viewport (or the visible zone on the display) have been parted to five variations just as comes after:
Extra small-- widths under 544px or 34em ( that appears to be the default measuring unit for Bootstrap 4
.col-xs-*Small – 544px (34em) and over until 768px( 48em )
.col-sm-*Medium – 768px (48em ) and over until 992px ( 62em )
.col-md-*Large – 992px ( 62em ) and over until 1200px ( 75em )
.col-lg-*Extra large-- 1200px (75em) and whatever bigger than it
.col-xl-*While Bootstrap works with
emrempxWatch exactly how aspects of the Bootstrap grid system perform across several gadgets having a functional table.
The brand-new and various from Bootstrap 3 here is one additional width range-- 34em-- 48em being assigned to the
xsAll the components styled using a particular viewport width and columns take care of its size in width with regard to this viewport and all above it. Whenever the width of the display screen gets under the specified viewport size the features pile above each other filling all width of the view .
You are able to also designate an offset to an aspect by a defined variety of columns in a certain display screen sizing and on top of this is done with the classes
.offset- ~ size ~ - ~ columns ~.offset-lg-3.col- ~ size ~-offset- ~ columns ~A couple details to think about whenever creating the markup-- the grids containing columns and rows ought to be placed within a
.container.container.container-fluidPrimary kins of the containers are the
.rowAuto format columns
Incorporate breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Bring in any quantity of unit-less classes for every breakpoint you need and each and every column will be the equivalent width.
Equivalent size
For instance, right here are two grid layouts that apply to every device and viewport, from
xs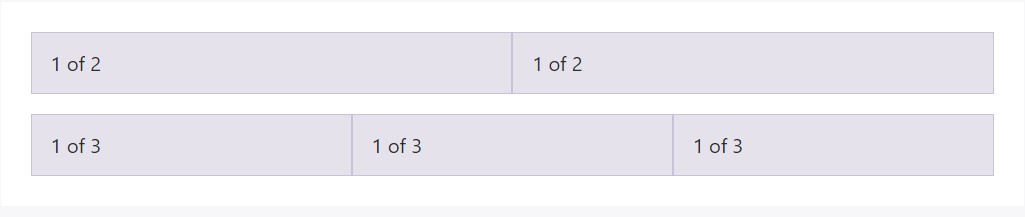
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Putting one column width
Auto-layout for the flexbox grid columns also means you can establish the width of one column and the others will immediately resize all around it. You may possibly work with predefined grid classes ( while revealed below), grid mixins, or inline widths. Note that the other columns will resize no matter the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable width material
Using the
col- breakpoint -auto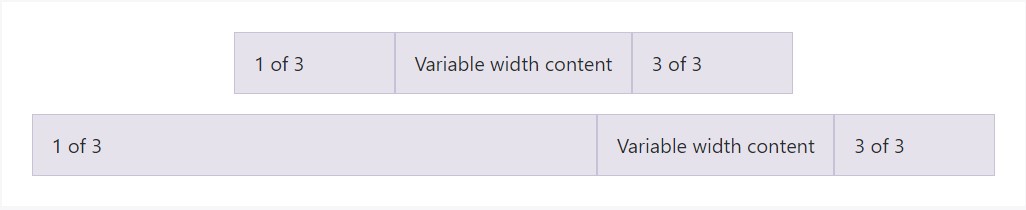
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Identical width multi-row
Build equal-width columns that extend multiple rows via adding a
.w-100.w-100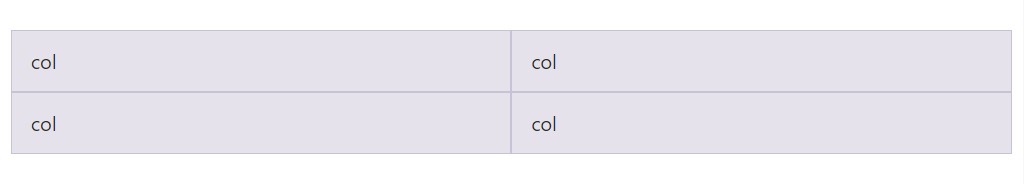
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>Responsive classes
Bootstrap's grid provides five tiers of predefined classes in order to get building complex responsive designs. Customise the size of your columns upon extra small, small, medium, large, or possibly extra large devices however you want.
All of the breakpoints
To grids that are the same from the smallest of devices to the largest, use the
.col.col-*.col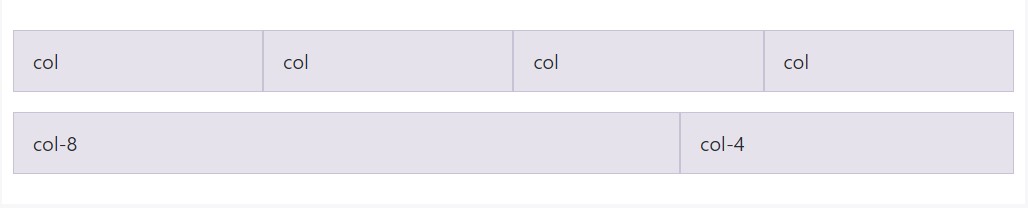
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8">col-8</div>
<div class="col-4">col-4</div>
</div>Stacked to horizontal
Employing a particular set of
.col-sm-*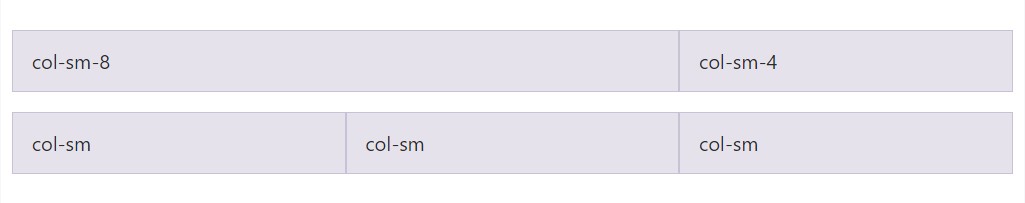
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-8">col-sm-8</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">col-sm-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
<div class="col-sm">col-sm</div>
</div>Combine and fit
Do not like your columns to simply stack in a number of grid tiers? Utilize a combination of different classes for each and every tier as needed. View the good example below for a more effective idea of precisely how everything acts.
<div class="row">
<div class="col col-md-8">.col .col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<!-- Columns start at 50% wide on mobile and bump up to 33.3% wide on desktop -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<!-- Columns are always 50% wide, on mobile and desktop -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
</div>Placement
Apply flexbox placement utilities to vertically and horizontally coordinate columns. ( useful reference)
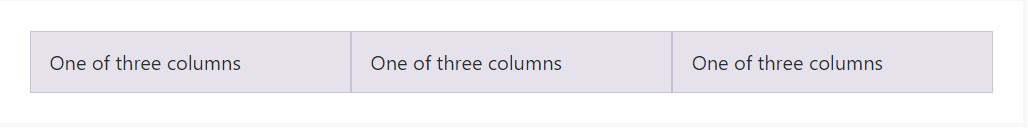
Vertical arrangement
<div class="container">
<div class="row align-items-start">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row align-items-center">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row align-items-end">
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col align-self-start">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col align-self-center">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col align-self-end">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
</div>Horizontal placement

<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-start">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-center">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-end">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-around">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
<div class="row justify-content-between">
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
<div class="col-4">
One of two columns
</div>
</div>
</div>No spacing
The gutters among columns inside our predefined grid classes may be taken out with
.no-guttersmargin.rowpaddingHere is simply the source code for generating these kinds of designs. Note that column overrides are scoped to just the first children columns and are intended by means of attribute selector. While this creates a further specific selector, column padding can easily still be more customised together with spacing utilities.
.no-gutters
margin-right: 0;
margin-left: 0;
> .col,
> [class*="col-"]
padding-right: 0;
padding-left: 0;In practice, here's specifically how it looks like. Bear in mind you can continue to apply this along with all of various other predefined grid classes ( featuring column widths, responsive tiers, reorders, and furthermore ).

<div class="row no-gutters">
<div class="col-12 col-sm-6 col-md-8">.col-12 .col-sm-6 .col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>Column covering
Assuming that in excess of 12 columns are settled inside a single row, each set of additional columns will, as one unit, wrap onto a new line.

<div class="row">
<div class="col-9">.col-9</div>
<div class="col-4">.col-4<br>Since 9 + 4 = 13 > 12, this 4-column-wide div gets wrapped onto a new line as one contiguous unit.</div>
<div class="col-6">.col-6<br>Subsequent columns continue along the new line.</div>
</div>Reseting of the columns
With the selection of grid tiers provided, you are certainly expecteded to bump into problems where, at certain breakpoints, your columns do not clear pretty suitable being one is taller in comparison to the various other. To take care of that, make use of a combination of a
.clearfix
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<!-- Add the extra clearfix for only the required viewport -->
<div class="clearfix hidden-sm-up"></div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-3">.col-6 .col-sm-3</div>
</div>Besides column cleaning at responsive breakpoints, you may have to reset offsets, pushes, or else pulls. Discover this in action in the grid scenario.

<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-5 col-md-6">.col-sm-5 .col-md-6</div>
<div class="col-sm-5 offset-sm-2 col-md-6 offset-md-0">.col-sm-5 .offset-sm-2 .col-md-6 .offset-md-0</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-5 col-lg-6">.col.col-sm-6.col-md-5.col-lg-6</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-5 offset-md-2 col-lg-6 offset-lg-0">.col-sm-6 .col-md-5 .offset-md-2 .col-lg-6 .offset-lg-0</div>
</div>Re-ordering
Flex order
Make use of flexbox utilities for handling the visible disposition of your content.
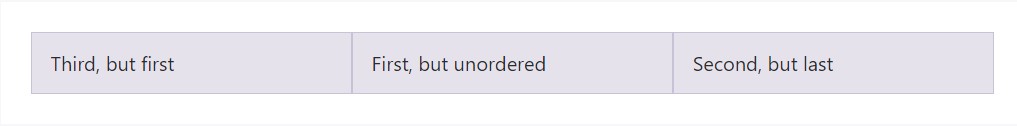
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col flex-unordered">
First, but unordered
</div>
<div class="col flex-last">
Second, but last
</div>
<div class="col flex-first">
Third, but first
</div>
</div>
</div>Offsetting columns
Transport columns to the right employing
.offset-md-**.offset-md-4.col-md-4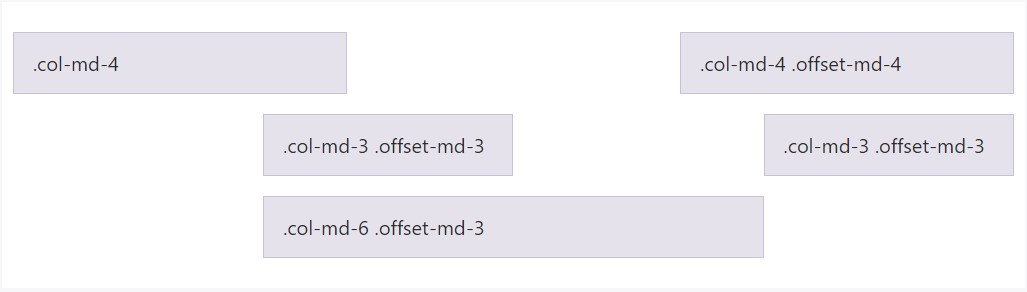
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 offset-md-4">.col-md-4 .offset-md-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 offset-md-3">.col-md-3 .offset-md-3</div>
<div class="col-md-3 offset-md-3">.col-md-3 .offset-md-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3">.col-md-6 .offset-md-3</div>
</div>Pushing and pulling
Easily switch the ordination of our incorporated grid columns together with
.push-md-*.pull-md-*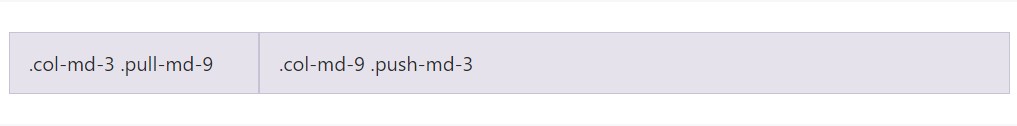
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-9 push-md-3">.col-md-9 .push-md-3</div>
<div class="col-md-3 pull-md-9">.col-md-3 .pull-md-9</div>
</div>Material placing
To roost your web content with the default grid, add a brand new
.row.col-sm-*.col-sm-*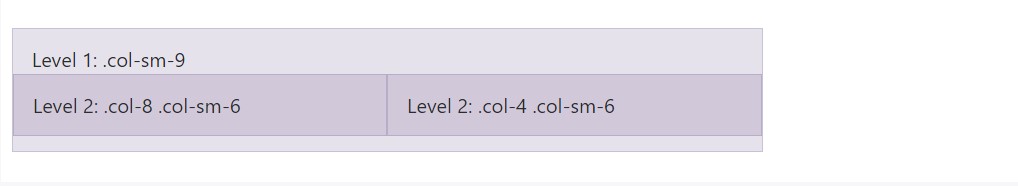
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Using Bootstrap's resource Sass information
When applying Bootstrap's source Sass data, you have the alternative of using Sass variables and mixins to make custom, semantic, and responsive webpage formats. Our predefined grid classes use these same variables and mixins to supply a whole set of ready-to-use classes for fast responsive designs .
Possibilities
Variables and maps control the variety of columns, the gutter size, as well as the media query factor. We utilize these to generate the predefined grid classes detailed earlier, as well as for the custom-made mixins listed below.
$grid-columns: 12;
$grid-gutter-width-base: 30px;
$grid-gutter-widths: (
xs: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
sm: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
md: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
lg: $grid-gutter-width-base, // 30px
xl: $grid-gutter-width-base // 30px
)
$grid-breakpoints: (
// Extra small screen / phone
xs: 0,
// Small screen / phone
sm: 576px,
// Medium screen / tablet
md: 768px,
// Large screen / desktop
lg: 992px,
// Extra large screen / wide desktop
xl: 1200px
);
$container-max-widths: (
sm: 540px,
md: 720px,
lg: 960px,
xl: 1140px
);Mixins
Mixins are employed with the grid variables to produce semantic CSS for individual grid columns.
@mixin make-row($gutters: $grid-gutter-widths)
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
@each $breakpoint in map-keys($gutters)
@include media-breakpoint-up($breakpoint)
$gutter: map-get($gutters, $breakpoint);
margin-right: ($gutter / -2);
margin-left: ($gutter / -2);
// Make the element grid-ready (applying everything but the width)
@mixin make-col-ready($gutters: $grid-gutter-widths)
position: relative;
// Prevent columns from becoming too narrow when at smaller grid tiers by
// always setting `width: 100%;`. This works because we use `flex` values
// later on to override this initial width.
width: 100%;
min-height: 1px; // Prevent collapsing
@each $breakpoint in map-keys($gutters)
@include media-breakpoint-up($breakpoint)
$gutter: map-get($gutters, $breakpoint);
padding-right: ($gutter / 2);
padding-left: ($gutter / 2);
@mixin make-col($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
flex: 0 0 percentage($size / $columns);
width: percentage($size / $columns);
// Add a `max-width` to ensure content within each column does not blow out
// the width of the column. Applies to IE10+ and Firefox. Chrome and Safari
// do not appear to require this.
max-width: percentage($size / $columns);
// Get fancy by offsetting, or changing the sort order
@mixin make-col-offset($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
margin-left: percentage($size / $columns);
@mixin make-col-push($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
left: if($size > 0, percentage($size / $columns), auto);
@mixin make-col-pull($size, $columns: $grid-columns)
right: if($size > 0, percentage($size / $columns), auto);Example utilization
You are able to transform the variables to your own custom made values, or else simply use the mixins using their default values. Here is literally an instance of using the default setups to build a two-column layout with a gap between.
Check it out in action in this particular delivered good example.
.container
max-width: 60em;
@include make-container();
.row
@include make-row();
.content-main
@include make-col-ready();
@media (max-width: 32em)
@include make-col(6);
@media (min-width: 32.1em)
@include make-col(8);
.content-secondary
@include make-col-ready();
@media (max-width: 32em)
@include make-col(6);
@media (min-width: 32.1em)
@include make-col(4);<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="content-main">...</div>
<div class="content-secondary">...</div>
</div>
</div>Customing the grid
Working with our integral grid Sass variables and maps , it is definitely possible to totally modify the predefined grid classes. Shift the number of tiers, the media query dimensions, and also the container sizes-- and then recompile.
Gutters and columns
The quantity of grid columns and also their horizontal padding (aka, gutters) can be modified via Sass variables.
$grid-columns$grid-gutter-widthspadding-leftpadding-right$grid-columns: 12 !default;
$grid-gutter-width-base: 30px !default;
$grid-gutter-widths: (
xs: $grid-gutter-width-base,
sm: $grid-gutter-width-base,
md: $grid-gutter-width-base,
lg: $grid-gutter-width-base,
xl: $grid-gutter-width-base
) !default;Features of grids
Going further the columns themselves, you may additionally modify the number of grid tiers. In the event that you desired only three grid tiers, you would certainly improve the
$ grid-breakpoints$ container-max-widths$grid-breakpoints: (
sm: 480px,
md: 768px,
lg: 1024px
);
$container-max-widths: (
sm: 420px,
md: 720px,
lg: 960px
);When making any type of changes to the Sass maps or variables , you'll need to save your modifications and recompile. Doing this are going to out a brand new package of predefined grid classes for column widths, offsets, pushes, and pulls. Responsive visibility utilities will additionally be up-dated to utilize the custom-made breakpoints.
Conclusions
These are in fact the undeveloped column grids in the framework. Using particular classes we can certainly tell the individual features to span a established number of columns baseding on the definite width in pixels of the viewable space in which the webpage gets featured. And given that there are actually a numerous classes defining the column width of the components instead of exploring every one it is certainly more effective to try to learn just how they certainly get put up-- it is undoubtedly very easy to remember having simply a few things in mind.
Inspect several online video tutorials relating to Bootstrap grid
Linked topics:
Bootstrap grid main information
W3schools:Bootstrap grid tutorial
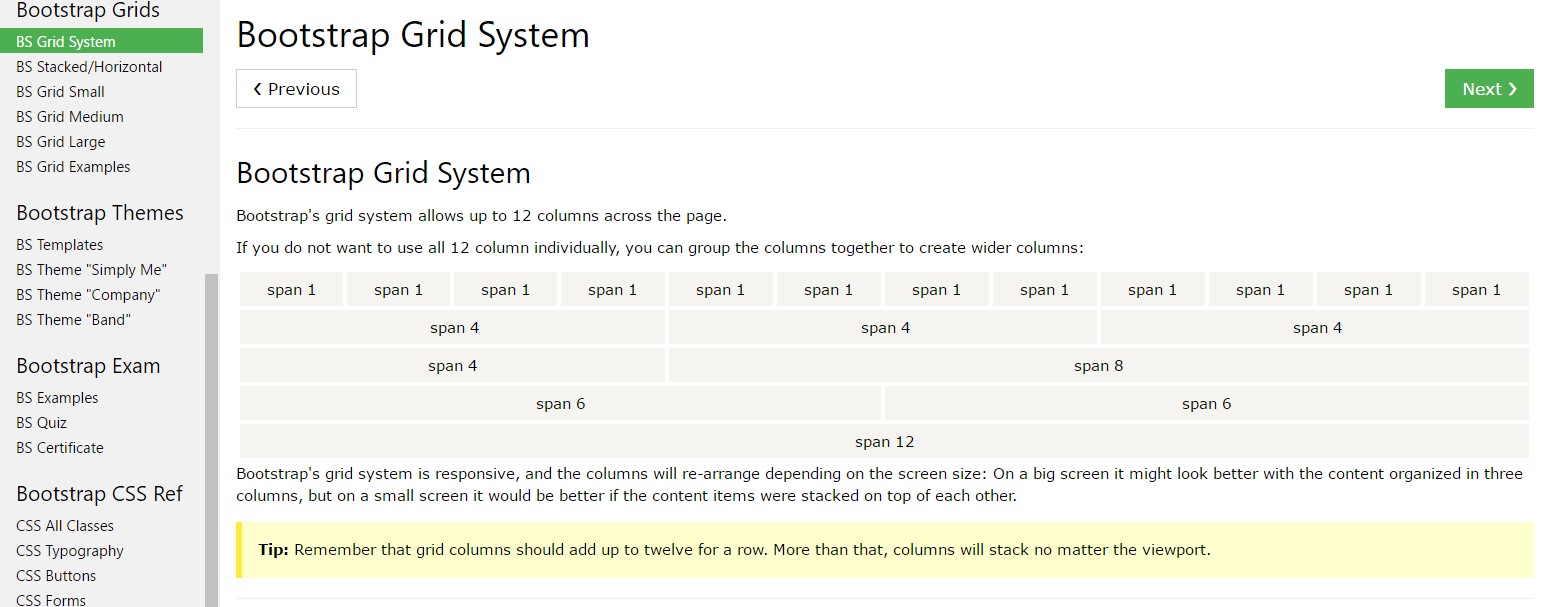
Bootstrap Grid column